Open Access
Creative Commons licenses
What are CC licenses?
As the author of a scientific text, you decide when, how, by whom and for what purpose your text can be used.
Creative-Commons (CC) licenses are standardized contracts with which you, as the author, determine how your work can be reused.
The license is valid as long as a work is protected by copyright - up to 70 years after the death of the author.
Once a license has been granted, it cannot be withdrawn. Restrictive licenses can be replaced by more open licenses.
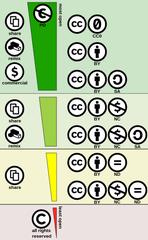
System of CC licenses
The combination of license terms allow for a number of different CC-BY licenses.
With each of these licenses, you have the right to acknowledge authorship.
Open
CC-BY allows unrestricted redistribution and use
Non-commercial
CC-BY-NC (non commercial) allows only non-commercial redistribution and use.
Restrictive
CC-BY-ND (no derivativs) only allows redistribution - with the addition of NC only non-commercial redistribution.
Declaration
Publications are marked with the appropriate icon, the reference to the license and a link, e.g.:

Diese Publikation steht unter der Creative-Lizenz CC-BY 4.0
This work is licensed under a CC-BY 4.0 license.
This work is licensed under a CC-BY 4.0 license. To view a copy of this license, visit https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0
Research Funding
Requirements
The Swiss National Science Foundation SNSF, like many other funding agencies (cOAlition S), requires that publications resulting from projects it funds (project submission as of January 2023) be published with a CC license.
Contributions to journals
CC-BY
Books and book chapters
CC-BY (recommended), more restrictive licenses like CC-BY-NC or CC-BY-NC-ND are possible
Rights Retention
The SNSF has adopted the "Rights Retention Strategy" developed by the cOAlition S. Researchers must indicate a rights retention for the post-review revised version when submitting a journal article with the following passage:
"This research was funded in whole or in part by the Swiss National Science Foundation (SNSF) [Grant number]. For the purpose of Open Access, a CC BY public copyright licence is applied to any Author Accepted Manuscript (AAM) version arising from this submission."
Contracs
Do not sign over the exclusive and unlimited rights to your texts sto your publisher. Insist on a license that allows you to fulfill your obligation to your funder and your university.
We are happy to assist you - feel free to get in touch before you sign your contract.
Swiss National Strategy on Open Access
At the end of 2015, the State Secretariat for Education, Research and Innovation (SERI) commissioned swissuniversities and the Swiss National Science Foundation (SNSF) to devise a national strategy for Open Access publications. The Open Access Strategy envisions that all publicly funded publications will be freely accessible by 2024.
Further information can be found here.
Open Access Policy of the University of Bern
The University of Bern supports Open Access as described in the Berlin Declaration on Open Access to Knowledge in the Sciences and Humanities which it signed in 2007, and declares that Open Access is a strategic objective. The Open Access Policy is in line with the Open Access Guidelines of the Rectors' Conference of the Swiss Universities (CRUS), the Swiss National Science Foundation (SNSF) and the Swiss Academy of Humanities and Social Sciences (SAGW); it does not interfere with the free choice of publication media or with academic freedom. The University has approved the following guidelines:
- The University of Bern requires its researchers to deposit a full version of all peer-reviewed and published academic work and the corresponding bibliographical information in the institutional repository of the University of Bern. This makes the academic work publicly available through Open Access, provided that there are no legal obstacles.
- The University of Bern encourages its researchers to publish their research results in Open Access journals, where appropriate journals exist.
- As of the 2014 reporting year, research evaluation and academic reports at the University of Bern are supported by the institutional repository of the University of Bern.
The University of Bern supports the implementation of these guidelines by operating an institutional repository which allows the University’s researchers to deposit their publications and the corresponding metadata.
Clarifications on practical implementation:
- In relation to publishers, researchers retain the right to make their publications publicly accessible via the University of Bern repository – after the expiry of any applicable embargo period.
- If this option is not available, the bibliographical information of the publications is deposited together with a full version of the text, which is protected from public access in the repository.
Open-Access-Policy
Support for alternative Open Access initiatives
In accordance with the LERU petition and the DORA initiative, Bern University Library supports alternative, non-profit Open Access initiatives.
Bern University Library currently supports the following initiatives:
- ArXiv
- Ephemera
- Knowledge Unlatched
- Language Science Press
- Open Book Publishers
- Open Knowledge Maps
- Open Library of Humanities
- Punctum Books
- SciPost
- Sui Generis
- SwissCOSS
Bern University Library is a member of:
If you know of an OA initiative that should be supported contact us.
Events
Events
Upcoming events on the topic of Open Access can be found on our main page or under "Services".
Helpful tools and websites
General information
- Open-Access.net is a central resource for all things Open Access (OA). It covers a wide range of disciplines and caters to many target groups.
Finding open access content
- Base is a search engine specialized in finding scholarly web-documents, particularly full texts in OA. The search engine is maintained according to scientific standards and those set by the OA-community.
- CORE is a meta-search engine that aims at the searchability of all OA-materials from repositories and journals worldwide. Both metadata and content can also be accessed via an application programming interface (API).
- Open Knowledge Maps is a non-commercial graphic explorer that offers a fast overview of any given research topic and shows central concepts and related discussions. It builds on the metadata from the search engines BASE and PubMed.
- Directory of Open Access Books is an international database for OA books in all disciplines. All works are peer-reviewed. DOAB features big publishing houses such as Springer, Taylor & Francis, or De Gruyter as well as smaller publishing houses and university presses.
- PubMedCetral is a full-text repository for medical, biomedical and other life-science research.
- DART Europe is a search portal to find European dissertations. The University of Bern's OA dissertations on BORISTheses are also indexed.
-
On Swisscovery Universität and PH Bern we ingest OA content from the following sources:
- BORIS
- BORIS Thesis
- BOP Serials
- DOAB
- DOAJ
- ROAD
- OApen
- Unpaywall
Where and how can I publish in OA?
- Directory of Open Access Journals is a central index of OA-Journals in all disciplines. In order to get listed, journals undergo a very strict review process. This is an ideal entry-point to find a suitable OA-Journal. Try the "Browse Subjects" function!
- Sherpa/Romeo is an aggregator collecting and analyzing OA information of journal publishers worldwide. The information is then published for each journal in a short summary that tells users everything they need to know about embargo periods, licenses and self-archiving options of any given journal.
- ThinkCheckSubmit helps researchers find trustworthy journals and decide what to do about predatory publishers. The website offers checklists and other instruments.
Browser extensions for quick OA Access
These extensions indicate whether an article a user is viewing online is available in OA: OA Button and Unpaywall for Chrome und Firefox, Open Access Helper for Safarii.